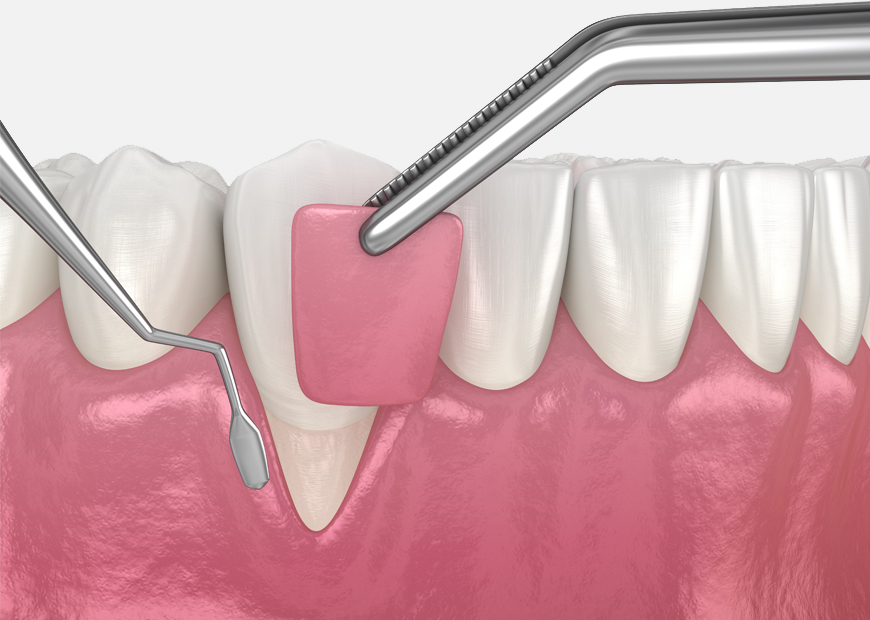
Gum grafts are used to cover exposed root surfaces due to excessive gingival recession. Generally, gum tissue is taken from the palate (the donor site) and stitched onto the exposed root surface (recipient site). The graft eventually gets integrated into the recipient site. Gum grafting can be done for one tooth or for several teeth. It is important to note that not all areas of recession can be grafted.
Gum graft surgery is utilised to provide an increased band of firm gum tissue (also known as attached gingiva) around the tooth that will provide greater resistance to further gum loss in the area. As a bonus, some of the gum that was previously lost can also be regained although it is not always possible to regain all the lost gum tissue. Sensitivity caused by exposed root surfaces is also reduced following gum grafting surgery. If the recession is in an aesthetic area then the aesthetics of the area can also be greatly improved.